The diameter of Earth is not just a number; it represents the vastness of our planet and offers insights into its structure and formation. Understanding this measurement is crucial for various scientific fields, including geology, astronomy, and environmental science. The diameter of Earth serves as a foundation for many calculations, such as gravitational forces, orbital mechanics, and even climate modeling. From the equator to the poles, Earth's diameter varies slightly due to its oblate spheroid shape, which has intrigued scientists for centuries. This article delves into the significance of the diameter of Earth, exploring its implications and answering some common questions surrounding this fascinating topic.
The Earth's diameter plays a vital role in our understanding of the planet's size and shape. Knowing the diameter helps us comprehend the scale of Earth in relation to other celestial bodies and the universe. Furthermore, this knowledge equips us with the tools to explore Earth’s geology, climate, and atmosphere. As we journey through this article, we will address some of the key questions regarding the diameter of Earth and its impact on our daily lives.
In this exploration, we will also touch upon the historical perspectives on Earth's diameter, the methods used to measure it, and how advancements in technology have refined our understanding. As we venture deeper, we will uncover the significance of Earth's diameter in various scientific fields and its relevance in contemporary discussions about planetary exploration and environmental sustainability.
What is the Diameter of Earth?
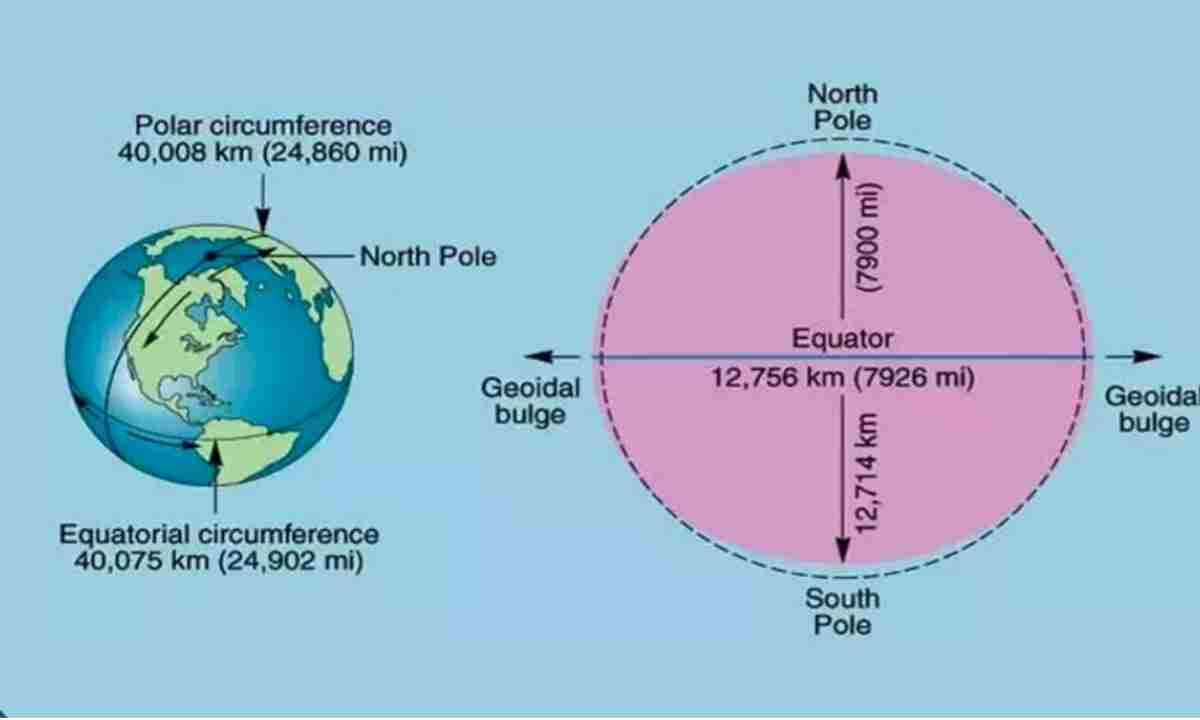
The diameter of Earth is defined as the distance across the planet through its center. It measures approximately 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles) at the equator and about 12,714 kilometers (7,900 miles) from pole to pole. This slight difference is due to the Earth's oblate shape, which causes it to bulge at the equator.
How is the Diameter of Earth Measured?
The measurement of Earth's diameter has evolved over time, utilizing various techniques and technologies. Historically, ancient astronomers used simple geometric methods to estimate the size of the Earth based on celestial observations. Today, advanced satellite technology, laser ranging, and other sophisticated tools allow scientists to measure the diameter of Earth with remarkable precision.
Why Does the Diameter of Earth Matter?
The diameter of Earth is fundamental to various scientific fields. It impacts gravitational forces, which in turn affect everything from ocean tides to the motion of satellites. Understanding the diameter also aids in the study of Earth's internal structure and the dynamics of its atmosphere.
How Does the Diameter of Earth Compare to Other Planets?
When comparing the diameter of Earth to other planets in our solar system, it is essential to note that Earth ranks as the fifth largest planet. For example, Jupiter, the largest planet, has a diameter of about 139,820 kilometers (86,881 miles), while Mars has a diameter of approximately 6,779 kilometers (4,212 miles). These comparisons highlight the unique characteristics of our planet.
What Are the Implications of Earth's Diameter on Climate?
The diameter of Earth plays a significant role in climate patterns and atmospheric circulation. The size of the planet affects how sunlight is distributed, influencing temperature variations and weather systems. Understanding these dynamics is crucial in addressing climate change and its impacts on ecosystems around the world.
Can the Diameter of Earth Change Over Time?
While the diameter of Earth is relatively stable, it can experience minor fluctuations due to geological processes, such as tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions. Moreover, factors like glacial melting and seismic activity can affect the distribution of mass on the planet, leading to slight changes in the measured diameter.
Conclusion: The Diameter of Earth and Its Significance
In conclusion, the diameter of Earth is a critical measurement that enhances our understanding of our planet and its place in the universe. By examining the diameter of Earth, we gain insights into various scientific fields, including geology, climate science, and astronomy. As we continue to explore and study our planet, the knowledge gained from understanding its diameter will undoubtedly inform future discoveries and innovations.