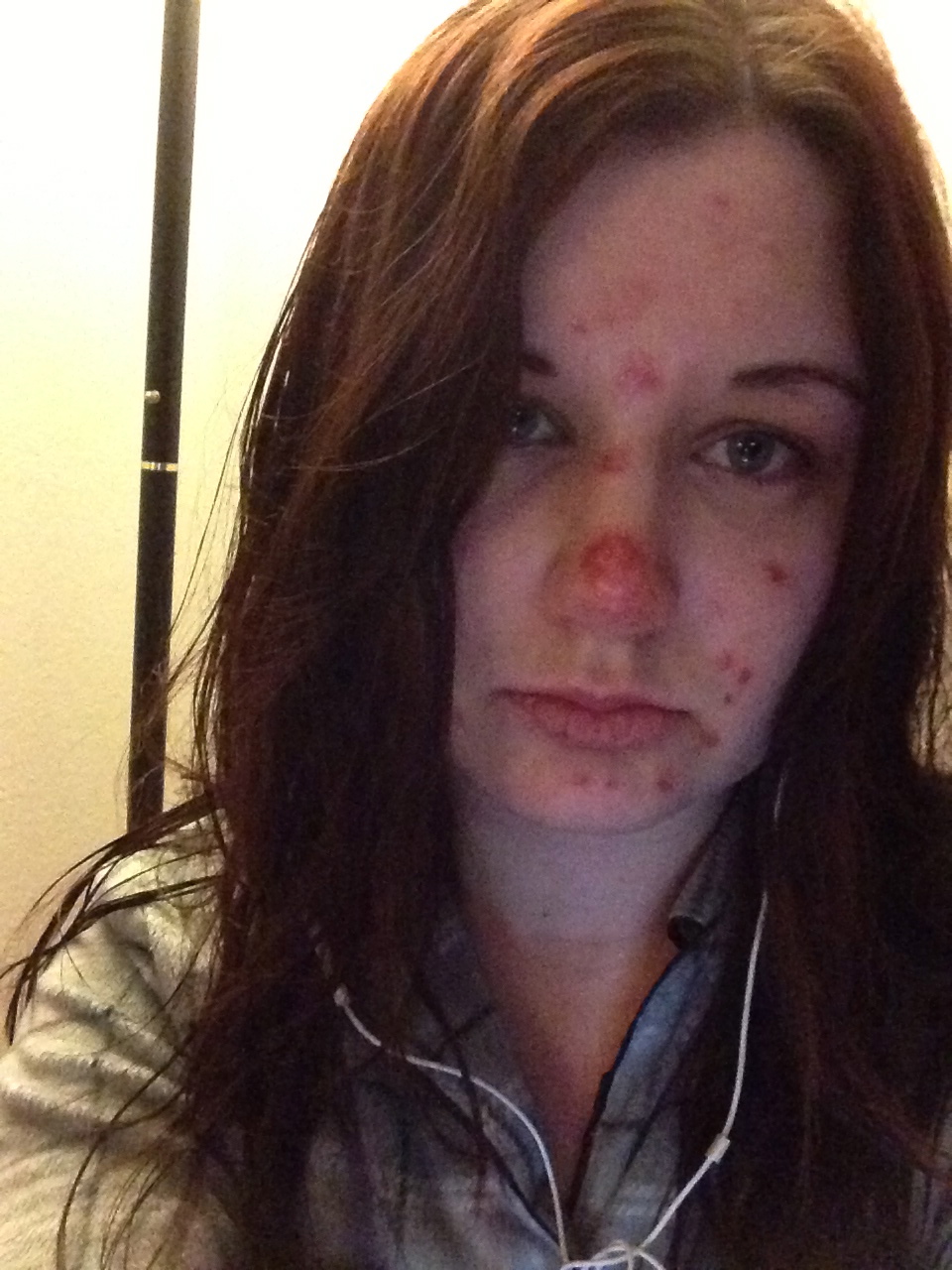
Dermatillomania, commonly referred to as skin picking disorder, is a mental health condition that affects many individuals, leading to significant emotional and physical consequences. This condition can manifest in various ways, often resulting in noticeable damage to the skin, which can exacerbate feelings of shame and anxiety. Understanding dermatillomania is crucial not only for those who suffer from it but also for their families and friends who wish to provide support.
The impact of dermatillomania can vary from person to person, with some experiencing mild symptoms while others face severe challenges that interfere with their daily lives. The disorder is classified under obsessive-compulsive and related disorders, indicating its complex nature and the challenges associated with treatment. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of dermatillomania, exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Whether you are seeking information for personal understanding or to support a loved one, this comprehensive guide on dermatillomania will provide valuable insights. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the disorder and the steps that can be taken to manage it effectively.
Table of Contents
- What is Dermatillomania?
- Symptoms of Dermatillomania
- Causes of Dermatillomania
- Diagnosis of Dermatillomania
- Treatment Options for Dermatillomania
- Self-Help Strategies
- Building Support Systems
- Conclusion
What is Dermatillomania?
Dermatillomania is characterized by the irresistible urge to pick at one’s skin, often leading to tissue damage. This condition is considered a form of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), where individuals feel compelled to engage in the behavior despite the negative consequences. Common targets for skin picking include the face, arms, and hands, but any area of the skin can be affected.
The American Psychiatric Association recognizes dermatillomania in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which highlights its legitimacy as a mental health disorder. Individuals with dermatillomania may engage in picking behaviors to relieve tension or anxiety, or they may feel a sense of pleasure from the act itself.
Symptoms of Dermatillomania
Symptoms of dermatillomania can vary widely among individuals but generally include:
- Frequent picking at the skin, often resulting in sores or scabs.
- Spending significant time engaging in skin picking behaviors.
- Feeling a sense of tension before picking and relief afterward.
- Hiding or avoiding situations where skin picking may be noticeable.
- Using various tools or objects to assist in picking.
In many cases, individuals with dermatillomania may also experience feelings of guilt or shame regarding their behavior, which can further complicate their mental health.
Causes of Dermatillomania
The exact causes of dermatillomania are not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors: There may be a hereditary component, as individuals with a family history of OCD or related disorders may be at higher risk.
- Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, trauma, or significant changes can trigger or worsen symptoms.
- Psychological Factors: Individuals with dermatillomania often struggle with anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem, which can exacerbate their need to pick at their skin.
Diagnosis of Dermatillomania
Diagnosing dermatillomania typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. The process may include:
- A detailed interview to understand the individual's symptoms and history.
- Assessment of the impact of skin picking on daily life.
- Utilization of standardized assessment tools to evaluate the severity of the disorder.
It is essential for individuals experiencing symptoms to seek professional help for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for Dermatillomania
Treatment for dermatillomania often includes a combination of therapies aimed at addressing the underlying psychological issues. Common treatment options include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is considered one of the most effective treatments for dermatillomania. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with skin picking.
- Medications: In some cases, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to help reduce the urges to pick.
- Habit Reversal Training: This behavioral technique helps individuals become more aware of their skin picking habits and teaches them alternative coping strategies.
Self-Help Strategies
In addition to professional treatment, individuals with dermatillomania can benefit from self-help strategies, including:
- Keeping Hands Busy: Engaging in activities that occupy the hands, such as knitting or using stress balls, can help reduce the urge to pick.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation and yoga can help manage anxiety and reduce the impulses to pick at the skin.
- Setting Goals: Establishing small, achievable goals for reducing skin picking can provide motivation and a sense of accomplishment.
Building Support Systems
Having a strong support system is crucial for individuals dealing with dermatillomania. Friends and family can play an essential role by:
- Providing understanding and encouragement.
- Helping to create an environment that minimizes triggers.
- Encouraging professional help and self-care practices.
Support groups, both in-person and online, can also provide a valuable space for individuals to share their experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion
Dermatillomania is a complex disorder that can significantly impact the lives of those affected. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively. If you or someone you know is struggling with dermatillomania, seeking professional help is a crucial step towards recovery.
We encourage you to leave comments, share this article, or explore further resources to enhance your understanding of dermatillomania. Together, we can foster a supportive community for those affected by this disorder.
References
1. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.).
2. National Institute of Mental Health. (2020). Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.
3. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Dermatillomania: Symptoms and Causes.