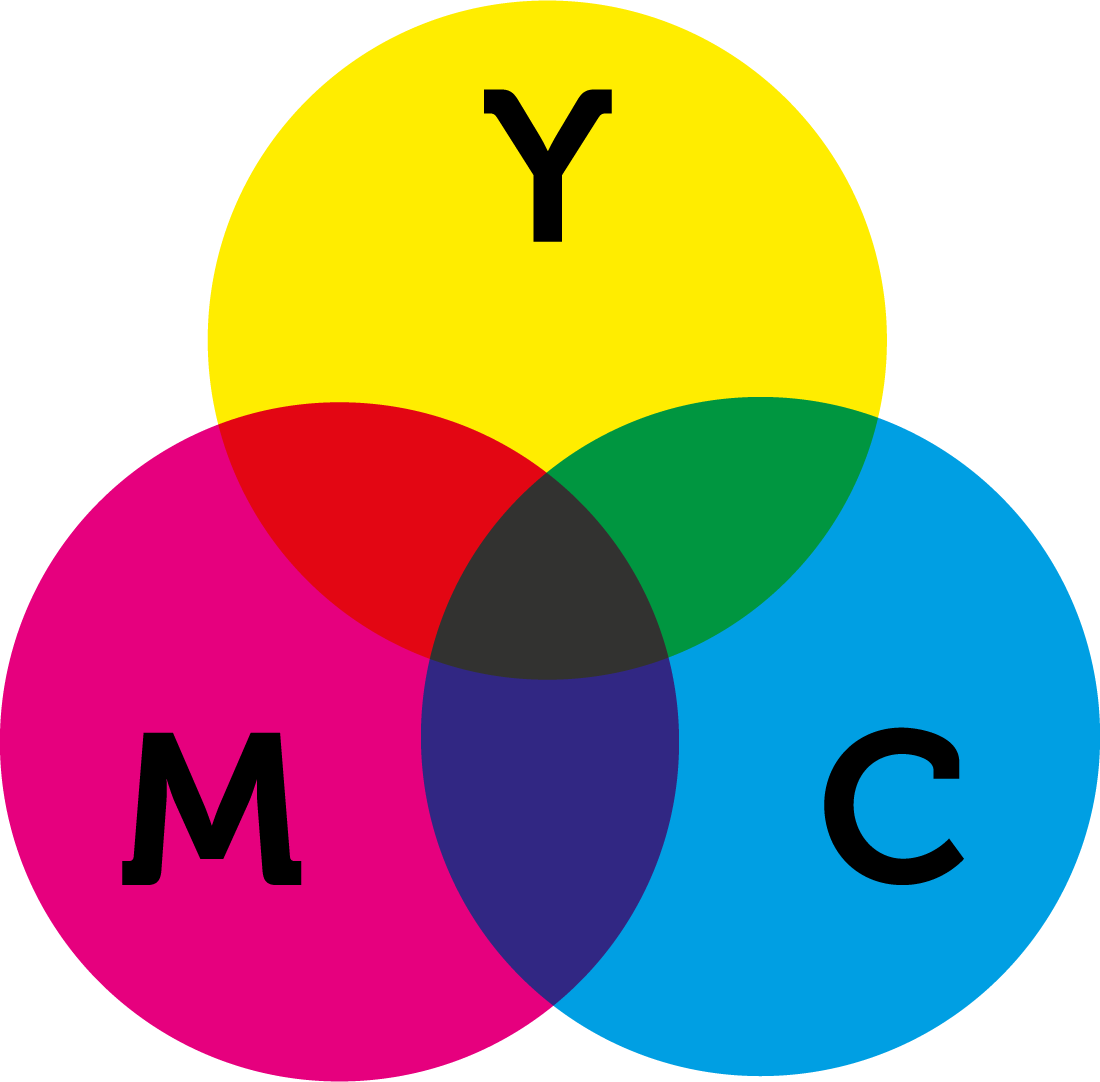
In the world of graphic design and printing, understanding color is crucial for achieving the desired results. One of the most widely used color models in this domain is CMYK, which stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). This model is essential for producing vibrant and accurate colors in printed materials, making it a fundamental concept for designers and printers alike. CMYK works by layering these four colors in various proportions to create a broad spectrum of hues. Each color is applied through a subtractive color mixing process, which means that the more ink you add, the darker the resulting color becomes.
The significance of CMYK extends beyond just color mixing; it also plays a crucial role in the printing process. When creating designs for print, graphic designers must convert their RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color schemes used for digital displays to CMYK to ensure that the printed product matches their vision. This conversion is vital as colors can appear drastically different on-screen compared to their printed counterparts.
As we delve deeper into the world of CMYK, we will explore its applications, advantages, and challenges. By understanding this color model, designers can enhance their skills and produce high-quality printed materials that effectively communicate their intended message. So, what exactly is CMYK, and how does it work in the realm of print design?
What is CMYK and How Does it Work?
CMYK is a color model that utilizes four primary colors—Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black)—to produce a wide range of colors through a subtractive process. This means that colors are created by subtracting varying amounts of light absorbed by the ink on paper. The more ink is applied, the darker the color becomes. The process involves layering the inks in different combinations to achieve the desired hue. For example, combining cyan and magenta produces blue, while combining magenta and yellow results in red.
Why is CMYK Important for Print Design?
CMYK is indispensable in print design for several reasons:
- Color Accuracy: Ensures that printed materials closely match the designer's original vision.
- Wide Color Range: Allows for the production of a vast array of colors needed for various design projects.
- Standardization: Provides a consistent framework for printers and designers to communicate color specifications.
How Does CMYK Compare to RGB?
CMYK and RGB are two distinct color models that serve different purposes. RGB (Red, Green, Blue) is an additive color model primarily used for digital displays, where colors are created by combining light. In contrast, CMYK is a subtractive model used for printing, where colors are created by mixing inks. This fundamental difference means that colors may look different when viewed on a screen versus in print, making it essential for designers to convert their designs from RGB to CMYK when preparing for print.
What Are the Advantages of Using CMYK?
Utilizing the CMYK color model in print design comes with several advantages:
- Cost-Effective: CMYK printing is often less expensive than other color printing methods, making it ideal for large print runs.
- High Quality: Provides rich and vibrant colors, ensuring high-quality printed materials.
- Compatibility: Widely accepted by most printing companies, ensuring seamless production.
Are There Any Limitations to CMYK?
While CMYK offers numerous benefits, it also has limitations:
- Color Gamut: Some bright colors, especially those in the RGB spectrum, cannot be accurately reproduced in CMYK.
- Complexity: Understanding the nuances of color mixing and conversion can be challenging for beginners.
- Print Variability: Factors such as paper type and printing method can affect the final color output.
How Can Designers Optimize CMYK Usage?
To achieve the best results when working with CMYK, designers should consider the following tips:
- Soft Proofing: Use software to simulate how colors will appear when printed.
- Monitor Calibration: Ensure that your monitor is calibrated to display colors accurately.
- Test Prints: Always request a proof before finalizing large print runs to check color accuracy.
What is the Future of CMYK in Design?
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CMYK in design remains promising. Advancements in printing technology, such as digital printing and inkjet technology, are expanding the possibilities for color reproduction. New inks and printing techniques are being developed to enhance color accuracy and expand the color gamut, allowing for more vibrant and diverse printed materials. However, the fundamental principles of CMYK will likely remain a cornerstone of print design, ensuring that designers can continue to create stunning visuals for years to come.
Conclusion: Embracing CMYK for Effective Print Design
In conclusion, CMYK is an essential color model for anyone involved in print design. By understanding its principles, advantages, and limitations, designers can create high-quality printed materials that effectively communicate their intended message. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing CMYK and staying informed about advancements in printing technology will be key to achieving success in the world of print design.